- Help & Advice
- Buying Guides
- Electrical Cable Buying Guide
Whether you're setting up a new electrical system or need to replace existing cables, understanding the different types of wires is crucial. You’ll need to consider what the cable is being used for and the risks and limitations of that cable, conductor and insulation material. You’ll also find the installation method can influence the performance, limitations, and rating.
An electrical wire is the electro technical component used to transport electricity to transmit energy and information. It’s made of a conductive material, single or multiple strands, often surrounded by insulating material. The inside of the electrical wire is called the “core”, which can be solid or stranded and often insulated with PVC. Flex is an abbreviation for Flexible Cable, meaning a cable that can flex repeatably, and is usually made up of multiple strands of wire. It’s a type of cable that is often used for connecting appliances to the mains.
Electrical cables have accreditations and standards that must be met. These verify that the design, electrical, mechanical, and material properties, as well as any specialist performance, meet the requirements outlined in all the standards that ensure they’re safe.
Mains cable colours are standardised across Europe and the UK, so they comply with international and British standards. Brown wires are live, blue wires are neutral, and green/yellow wires are the earth wires.
Types of Electrical Cable
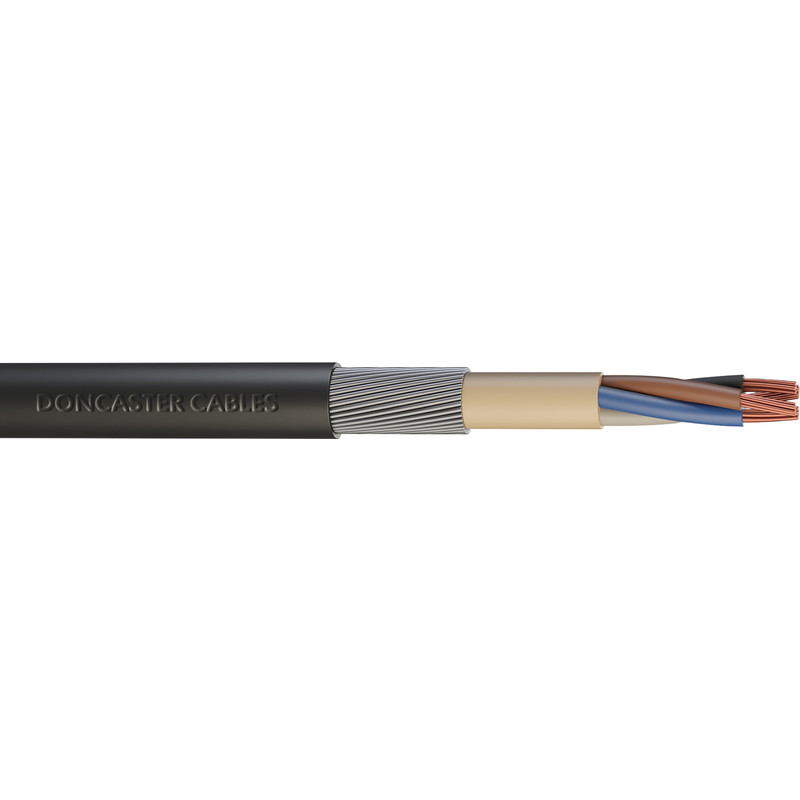

Steel Wire Armoured Cable
Steel wire armoured cable, commonly abbreviated as SWA, is a hard-wearing power cable designed for the supply of mains electricity and auxiliary control cable. Used for underground systems, cable networks, power networks, outdoor and indoor applications, and cable ducting. The SWA cable can also be referred to mains cable, power cable, armoured cable and booklet-armoured cable.
SWA Cable is designed to have mechanical protection, which is why the cable is often used for external use.
SWA Cable can be heavy, and its rigidity makes installation difficult in tight spaces because it doesn’t easily bend. SWA also comes at a higher cost compared to other cable types due to the extra mechanical protection it offers.
Advantages
-
Designed to have mechanical protection
-
Versatile
-
Reliable power transmission
Things to Consider
-
Heavy
-
Inflexible
-
Increased cost
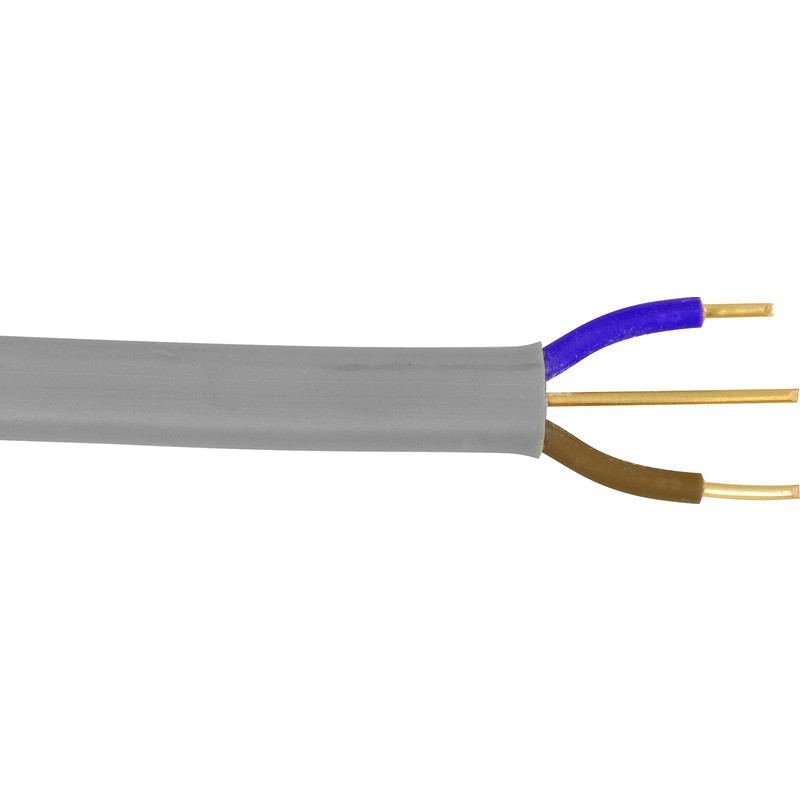
Twin and Earth Cable
Twin and Earth cable, also known as T&E cable or 6242Y cable, is a flat sheathed, fixed mains cable used in domestic and commercial situations. It has two insulated conductors (brown for live and blue for neutral) and an earth connector (CPC) in a PVC sheath. This cable is mainly used for lighting, power outlets, and switches.
The flat shape of 6242Y cable makes it easy to install, especially when running along surfaces or inside conduit. The colour-coded insulation of the conductors makes it easy to identify and connect the correct circuits when installing the cable. This reduces the risk of mistakes and ensures the correct electrical connections.
T&E cable is not suitable if it will be regularly moved or installed in an environment where it could be damaged. T&E is also not UV stable meaning it cannot be used outdoors.
Advantages
-
Easy to install
-
Colour coded conductors are easy to identify
-
Reduced risk of mistakes due to colour coded conductors
Things to Consider
-
No mechanical protection
-
Internal use only
-
Fixed use only
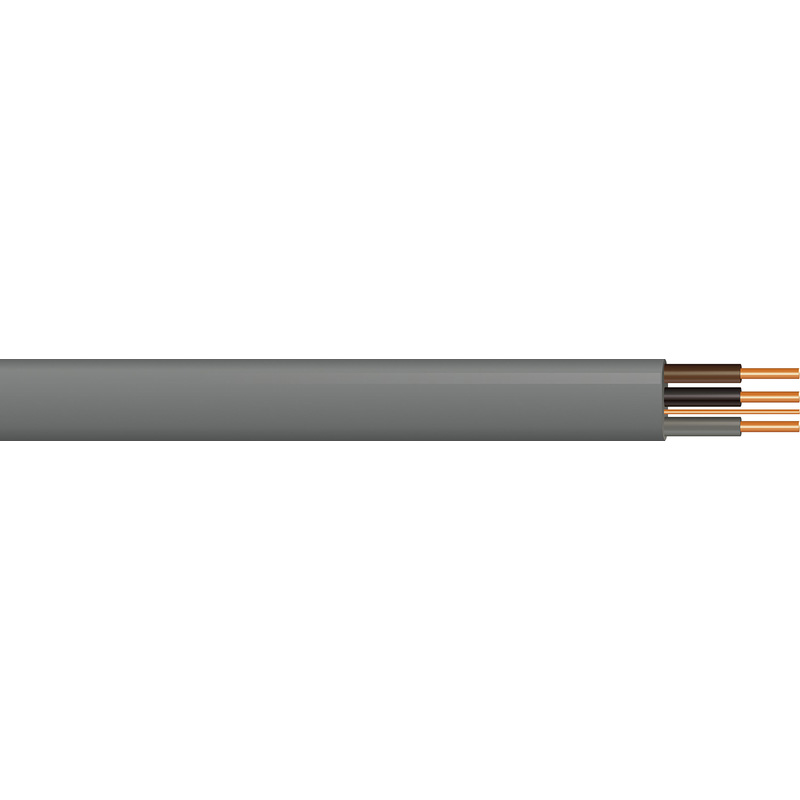
3 Core and Earth Cable
3 Core & Earth cable, also known as 6243Y cable, has three copper conductors – each insulated with PVC insulation – and a bare or insulated earth wire (CPC- Circuit Protective Conductor). These are held together in a PVC sheath.
The conductors are colour-coded so they can be easily identified, and they are ideal for general, domestic and light industrial mains wiring including lighting circuits, central heating, and extractor fans. 3 core & earth cable can be used in damp or dry conditions, on trays or boards, buried in plaster, or in channels.
6243Y cable offers little mechanical protection so cannot be buried deep underground or used outside. This cable is also only suitable for fixed use only, and isn’t suitable if it needs to be moved around from time-to-time.
Advantages
-
Additional conductor for two-way switching
-
Colour-coded conductors make installation safer and easier
Things to Consider
-
No mechanical protection
-
Internal use only
-
Fixed use only

Conduit Wiring Cable
Conduit wiring cable (also known as 6491X cable) is used in industrial and commercial situations, as well as in residential applications. 6491X Cable is suitable for power and lighting circuits and building wiring. The cable is intended for use in semi-flush exposed conduits and embedded conduits as well as in closed installation ducts, and is ideal for the internal wiring of appliances and apparatus.
Colour-coded insulation helps to prevent mistakes when wiring. As each conduit wiring cable is separate, they are easy to maintain and can be inspected, repaired and modified whenever needed.
Conduit wiring cable, like core & earth cables, offer little mechanical protection and can only be used inside.
Advantages
-
Colour coded for safer installation
-
Easy to maintain, inspect, repair and modify
Things to Consider
-
No mechanical protection
-
Internal use only
Heat Resistant Flex Cable
Heat resistant flex cable has three individually insulated conductors and a sheath made of silicone, PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene), or fibreglass which can withstand high temperatures.
Ideal for electrical appliances, heaters, extensions reels, tools and equipment that may be exposed to high temperatures. These cables are flexible, so they can be easily bent and routed to fit into tight spaces with a reduced risk of overheating. This flexibility means they’re more versatile and installation is easier.
Heat resistant flex cable comes at a higher price than non-heat resistant cables due to the specialist qualities they possess and the wider versatility.
Advantages
-
Flexible and durable
-
Versatile
-
Safe and reliable in locations where heat is a factor
Things to Consider
-
Higher price than non-heat resistant alternatives
Immersion Heater Cable
Immersion heater cables, also known as 3183TQ cables are flexible cords suitable for use in domestic premises, kitchens and offices. Also suitable for use in hot situations such as immersion heaters.
These cables are primarily used in heating systems such as boiler, central heating applications, and water heaters. You’ll find tinned copper conductors provide extra resistance to oil and grease.
When it comes to immersion heater cables, they have a limited number of applications they can be used in – as they are mainly used in heating systems.
Advantages
-
Safe and reliable in locations where heat is a factor
-
Tinned copper conductors provide extra resistance to oil and greas
Things to Consider
-
Limited applications
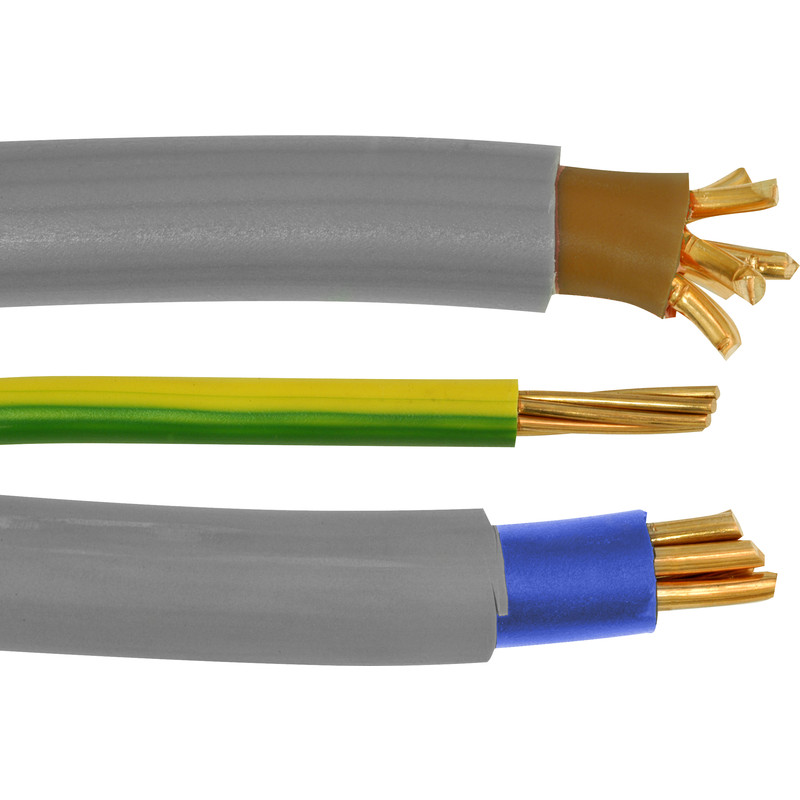
Meter Tails Cable
Meter tails cable, also known as 6181Y cable, connects the electricity meter to the electrical supply of a domestic property. These cables have insulated copper conductors which carry electricity from the meter to the main consumer unit. The size and length of the cable depends on the electrical requirements of the building and the distance between the meter and the consumer unit. BS7671 states meter tails should not exceed 3 meters.
These cables are an essential component of electrical systems, ensuring the proper flow of electricity from the meter to the main consumer. The cable is durable, built to withstand the demands of high electrical currents. Also, meter tails cables are available in a wide range of sizes and lengths, meaning they’re flexible for different buildings.
Meter tails cable, compared to other cables, have a relatively high cost per length.
Advantages
-
Durable
-
Essential component for electrical system
Things to Consider
-
Relatively high cost per length to other cables
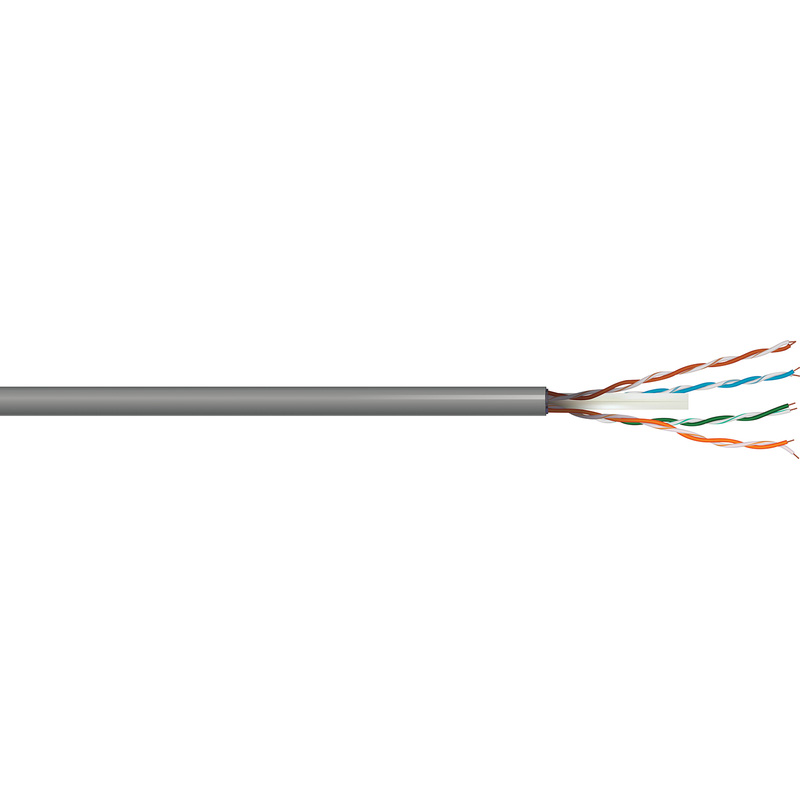
Data Cable
Data cables, also known as CAT5 or CAT6 cables, are used for network and broadband connections. They have 2 to 4 pairs of twisted conductors that are individually insulated with a PVC sheath. CAT6 cables can process more data than CAT5 and are used in large commercial properties, while CAT5E cables are more routinely used in residential and small business premises.
These cables are widely available and widely used, so they can be easily replaced and installed. Data cables are standardised and installation is relatively simple, ensuring a convenient and efficient setup of data connections.
CAT5 and CAT6 cables are widely used, however technology in this field is always evolving, and new versions with higher bandwidth are being introduced. This means the cables of today may not support future advancements in data transmission, potentially requiring upgrades or replacements, to avoid this it is advisable to use the latest data cables available with the highest specification. There is also the possibility of electromagnetic interference with other cables.
Advantages
-
Widely available and widely used
-
Installation is relatively simple
Things to Consider
-
Possibility of electromagnetic interference with other cables
-
Limited future proofing as technology improves
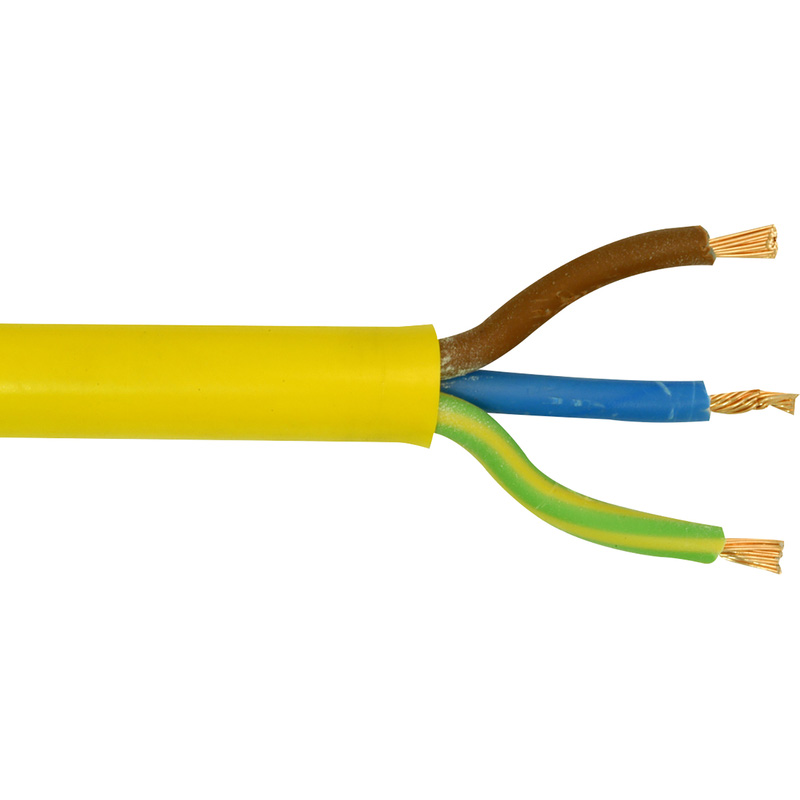
Arctic Cable
Arctic cable, also known as 3183A cable, is a specific type of specialist cable made with arctic grade insulation, designed to withstand very cold temperatures. It has three colour-coded cores and is designed to be used in cold environments, such as commercial, industrial, and construction settings where temperatures can get as low as -40 degrees Celsius.
The primary advantage of arctic cable is its suitability for extremely cold temperatures. The arctic grade insulation allows the cable to maintain its flexibility and functionality in sub-zero conditions. Also, the flexibility of the cable means it’s easier to install and can be manoeuvred around more easily compared to rigid cables.
Arctic cables have a higher cost than standard cables as they are manufactured using specialist material to make them suitable for very cold temperatures.
Advantages
-
Suitable for extremely cold temperatures
-
Arctic grade cable is very durable
-
Flexibility makes it easier to install
Things to Consider
-
Higher cost than standard cable
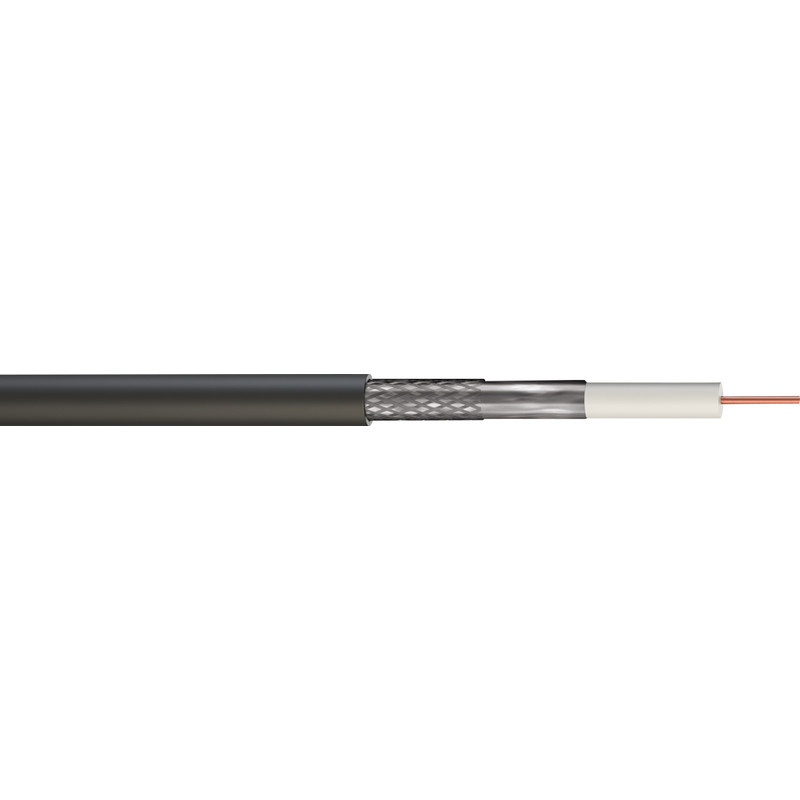

Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cable, also known as CT100, RG6 or coax cable, is used for transmitting radio frequency signals, usually for TV, satellite, CATV and CCTV. They have a single copper wire conductor surrounded by insulation. This is then encased by a woven metal braid – which shields against interference from other cables – and an outer insulating jacket. Coaxial cables use connectors plated with high-conductivity metals such as silver or gold for high signal transmission.
Coax cable is widely available and widely used, so can be easily replaced and repaired if it gets damaged. Coaxial cable is also durable and can withstand normal wear and tear. It also had excellent transmission over short distances.
The main consideration with coaxial cables is potential signal loss, which can occur over long distances. Coax cables are also not suited to exposure to the elements, so cannot be used outside.
Advantages
-
Widely available and widely used
-
Durable and can withstand normal wear and tear
-
Excellent transmission over short distances
Things to Consider
-
Not suited to exposure to the elements
-
Potential signal loss over long distances
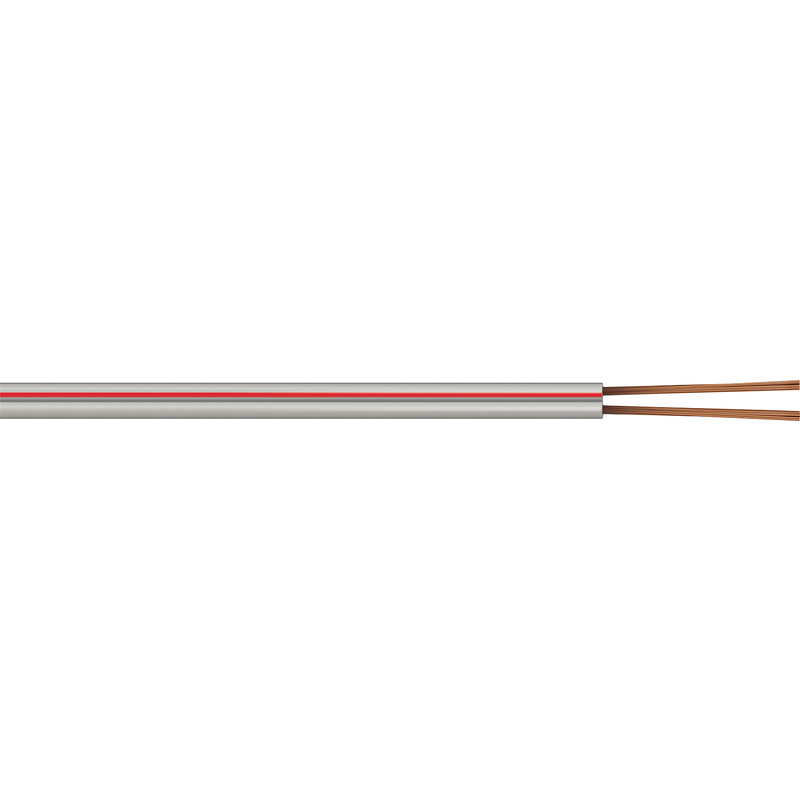
Bell Wire
Bell wire is a small, low voltage wire usually used for connecting a doorbell to a push button. It typically has a PVC sheath and consists of twin strand solid copper conductors. Bell wire is designed for low voltage applications such as doorbell chimes, call bells or buzzer systems where a small and flexible wire is required to get round tight corners and into small holes.
Bell wire is relatively low in cost, offering good value for low voltage & low current applications.
The main consideration with bell wire is that it’s limited to applications under 30 volts.
Advantages
-
Advantages
-
Small and flexible
-
Low cost
Things to Consider
-
Limited to 30v or less
Alarm Cable
Alarm cable is a type of low voltage cable commonly used in alarm security systems. It usually has multiple cores with each conductor insulated in a different colour and surrounded by a PVC sheath to protect the wiring.
A significant advantage of alarm cable is its flexibility, which makes it easy to handle and install.
Alarm cables are limited to 30v low voltage applications such as alarm systems, so they have limited versatility.
Advantages
-
Flexible and easy to install
-
Low cost
Things to Consider
-
Limited to low voltage applications
Speaker Cable
Speaker cable is a type of low voltage cable for carrying electrical current between a speaker or speakers and an amplifier. It is commonly used in home cinemas and surround sound systems, typically a speaker cable is made up of two stranded conductors which offer a low resistance.
Upgrading speaker cable in an audio setup can significantly improve sound quality. Speaker cables use stranded conductors which make the cable flexible, allowing for easy routing and installation.
Speaker cable has limited uses, as it’s only used for sound transmission.
Advantages
-
Improve sound quality of existing systems
-
Flexible
-
Easy to install and maintain
Things to Consider
-
Limited uses
Key Electrical Cable Features
Screening
Screening, also known as shielding, is a metallic layer placed over insulated conductors to stop electrical interference. There are three main types: unshielded, foil and braided. Unshielded has no screening, while foil screening uses aluminium or copper tape around the conductors which is cost effective and doesn’t add thickness. Braided screening uses metal wires braided around the conductors for flexibility and good coverage.
Approvals and Standards
Cables must adhere to the Building Regulations 2005 and the BS7671 wiring standards. Other cable standards include: BASEC, HAR, UL, DEF STAN, and REACH.
Some standards may apply depending on the specific wire and where it’ll be used. These regulatory and standard compliance measures ensure safety and quality in domestic wiring installations.
Low Smoke & Low Fume
In highly populated or enclosed public areas, Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) cables are necessary.
These specialist cables are designed to minimise the release of toxic fumes if there is a fire and therefore prevent fatalities from harmful smoke.
Size
Thicker conductors mean thicker cables, which can be challenging to install and less discreet. However smaller conductors carry less current, thin wires are suited to low current applications, while thicker conductors are better for high current applications.
The more conductors a cable has, the thicker the overall cable will be. You'll find that thicker cables are less malleable and more fiddly to install, but can be more durable.
Conductor Type
Solid core conductors are rigid and resistant to flexing, which is good for permanent wiring.
Stranded core conductors are flexible and withstand flexing, which is good if the cable will be regularly moved.
Length
The amount of wire you need depends on the space you're covering. Having excess wire is not ideal, but having too little can result in tight connections that could reduce their quality.
Finding a balance between comfortable connections and not having excess cable is key.
Colour
The UK colour code of insulated conductors in electrical wiring indicates their function: blue for neutral, brown for live, and Green/Yellow stripe for earth/CPC.
The outer sheath is typically black, white, or grey and serves as a basic protective covering.






